New generation basal insulin improves the patient's metabolic activity by 20%, reduces the risk of hypoglycemia and allows better control
It is estimated that 50% patients do not have control of their glycemic levels, among other factors, for fear of nocturnal hypoglycemia (weight gain, sweating, irritability, nightmares, cardiovascular risk, reduction in mental function and dementia), as an effectsecondary of some current treatments.Given this, specialists presented the new generation of insulins, for a customization of treatment and promotes adherence.
In Mexico, figures from the National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012 (Ensenut), points out only 25% of the 6.4 million Mexican adults diagnosed with diabetes has good metabolic control.This was discussed during the “The New Age of the Gold Standard: Insulina Glargina U300”, where national and international experts met to discuss the importance of the use of increasingly specialized treatments that allow both the control of glycemic levels, andAt the same time, improve the quality of the patient in the long term.
In that context, Dr. Guillermo González, Director & AMP;The main researcher at the Jalisco Institute for Research in Diabetes and Obesity, stressed that diabetes is a disease that represents an increase in risk factors such as overweight and obesity."Thanks to medical innovation, today we can count new basal insulins, which are focused on reducing the risk of hypoglycemia, improving metabolic activity and allowing better control in the patient's weight," he said.
Data from the World Health Organization (WHO) point out that there are currently about 318 million people in the world, with high glucose tolerance, which is a high risk of developing diabetes.Only in 2015 were 5 million deaths caused by this disease, according to the International Diabetes Federation (FID).
After blood pressure and smoking, diabetes is considered the third most important risk factor for premature mortality.Both the American Diabetes Association (AD), and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), indicate that an approach to the patient -centered disease is required, including treatments that thePersonalization according to the needs of the individual, which can help to have effective management and promote adherence to treatment.
During his participation in the Forum, Dr. Óscar Lozano, Endocrinology Endocrinology Consultant of Internal Medicine and Endocrinology at the National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition Salvador Zubirán, said that in the management of diabetes the initiation of insulin is oftendelays, "and despite the proven efficacy, insulin has been resisted by patients and doctors partly due to the risk of hypoglycemia."
In accordance, Dr. Rafael Campuzano, secretary of the Mexican Council of Endocrinology, said that even if patients begin insulin therapy, fear of hypoglycemia and the perception of lack of effectiveness during the first weeks after initiation or transitionThey can contribute to high abandonment rates.“All types of hypoglycemia, at any time of day or night, are inconvenient, terrifying and important to consider.Due to different myths, adherence to insulin therapy is generally poor and the interruption rate of insulin treatment increases over time. ”
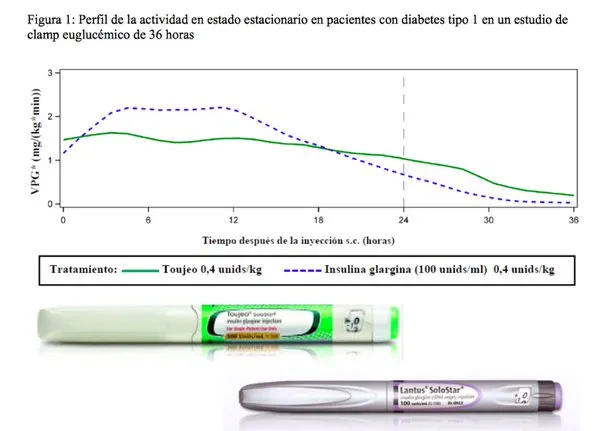
For his part, Dr. Fernando Lavalle, coordinator of the University Hospital of Monterrey, mentioned that progress in researchMedical have achieved improvements in the glycemic control of patients.“The new basal insulins allow up to 36 hours of glycemic control, which is a real innovation compared to standard treatments.This favors patients suffering from a third less of nocturnal hypoglycemia.Patients with type 1 diabetes can be applied up to 27 hours after the last injection, ”he said.
The objective of diabetes management is to bring blood glucose levels to the target4.However, approx.Half of patients, with or without insulin, are not reaching their glycemia control objective (glycemic).Despite the escalation of medication regimes, many patients may require insulin to achieve adequate glycemic control.
Maintaining good glycemic control at night is fundamental in patients with type 1 and 2 diabetes if the correct dose of insulin is not administered during the night period, their blood glucose levels could drastically increase from 2 to 4 in the morning,increasing the risk while the patient sleeps.
Finally, Dr. María Elena Sañudo, medical manager SANOFI, stressed that diabetes is one of the main chronic diseases with a high failure rate due to poor adhesion to treatment.“In Sanofi we are dealing with the needs of the population.We are putting all our experience and legacy as a company in this area, having launched the most studied insulin and now with this new generation insulin, which can help patients have greater adherence.And we continue to promote the investigation of solutions that improve people's lives. ”
He stressed that “the basal insulin for patients with type 1 diabetes is also focused at leveling the neutral effect on weight, and allows fluctuation of the patient's metabolic activity during the day, is 20% lower compared to othersInsulinsAdvances and innovation in the treatment of diabetes provide more safety and stability in patients with a lower number of injections, which is an improvement of their quality of life, ”he concluded.