Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease that is characterized by high blood sugar levels.
It originates because the body does not produce insulin or does not use it properly.
Insulin is a hormone necessary to transform food sugar into the energy we need to perform the activities of our daily lives.It is produced by the pancreas, which is an organ that is located in the left region of the abdomen.
After eating, some foods are transformed into glucose (sugar).
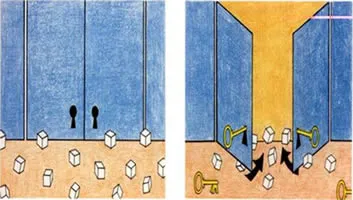
The glucose is transported by the blood to the body cells, where insulin "opens the door" as a key in the lock to enter them and fulfill the function of giving us energy.
When the amount of insulin is not enough, the door does not open and does not enter glucose to the cells so it remains in the blood and generates high hyperglycemia or blood glucose.
There are several types of diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus: usually occurs in childhood but may appear at any age.The pancreas stops producing insulin and originates from an autoimmune condition, that is, the immune system or organism defenses confuses the cells that produce insulin (beta cells of the pancreas) with strange cells, attacks and destroys them.
More information: Link
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus: It is the most common type of diabetes, mainly in overweight adults, sedentary, with a history of diabetes and now in children with obesity.The body does not produce sufficient amount of insulin or it does not act properly or a combination of both.
More information: Link
- Gestational diabetes: it manifests itself in pregnant women, more frequently in obese, with a family history of diabetes and usually disappears after childbirth.If it is not detected and controlled, it can produce alterations in the fetus, such as macrosomia or a baby with a lot of weight, problems during and after delivery.Many of the women who have had gestational diabetes later develop type 2 diabetes. A control is necessary at 6 (six) weeks after birth to know if I really have type 2 diabetes or not.
More information: Link
Other types of diabetes: as in pancreas diseases, etc.
More information: Link
The diagnosis of diabetes is performed with two blood glucose (sugar) tests in fasting blood or an oral glucose overload test (PTOG).If the blood glucose is equal to or greater than 126 mg/dl on an empty stomach in 2 opportunities or if it is equal to or greater than 200 mg/dl at 120 minutes in the PTOG you have the diagnosis of diabetes.
Some of the following symptoms may be present:
- Much thirst
- Excess urinating
- Tiredness, fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Excessive hunger
- Weight loss without an apparent cause.
- Stomach pain, nausea or vomiting.
Complications
High levels of glycemia permanently can cause long -term problems because small blood vessels called microvascular complications are damaged as well as large blood vessels called macrovascular complications.
Microvascular complications:
- Retinopathiabetics: It is the damage to the eyes.A background must be done once a year.
- Diabetic nephropathy: It is the affectation of the kidneys.The kidneys filter blood waste;When they don't work well, they can accumulateToxic substances.
- Neuropathiadiabetic: nerves of the whole body can be affected.
Macrovascular complications:
- Heart arteries causing acute myocardial infarction.
- Brain arteries causing stroke or brain infarctions.
- Arteries of the legs with pain when walking or coloration change of some of the fingers of the feet (gangrene).

This makes it very important to maintain your diabetes in the best possible condition with optimal blood sugar levels.
How to perform good control of your diabetes?
- Glycosylated hemoglobin: it is a blood test that gives a global panorama of its total blood blood glucose levels of the last 3 months.The acceptable value must be less than 7% to avoid chronic diabetes complications .If the value is superior, it means that its glycemia remained high during that period of time.
Your doctor must request a glycosylated hemoglobin every 3 months.
- Blood voltage: The ideal values must be less than 130/80 mmhg .If it is greater, it makes your heart work more than it due.
- LDL cholesterol: o "bad" cholesterol must be less 100 mg/dl .This accumulates in the arteries and obstructs them.
It is important that he leaves the habit of smoking, contributes to the progression of chronic diabetes complications.

Remember that you are the main protagonist in the control of your diabetes.